Nowadays Russian heat power plants produce around 61 % of electrical power which is consumed in our country. The rest 39% is covered by hydro and atomic power plants. The share of old steam turbines of the Soviet period composes more than 85 %.
Modern combined gas-steam turbine blocks and gas turbine power plants makes up less than 15%.

Spare parts for old steam turbines are manufactured in the Russian Federation. After 2014 Russian Federation started implementation of the program for import substitution. The program means that most of components for the power and oil/gas industries must be produced in Russia. In this way the problem of import substitution for turbine spare parts production is practically solved.
It is well known that there was no production of big gas turbines in the USSR. That’s why there is no considerable power generation with old gas turbines in Russia.
It should be mentioned that spare parts for such gas turbine manufacturers as Siemens, General Electric, Solar Turbines, Kawasaki, Mitsubishi-Hitachi, Pratt Whitney, Rolls Royce and their packagers are not produced in Russia. They are produced and supplied mainly by foreign companies which manufacture turbines and make packages with them.

Electricity generation in Russia is based mostly on steam turbine blocks. The blocks of major cities operate in cogeneration mode. They provide steam for central heating fulfilling a great social function. In comparison with condensation turbines they work in heating but not in electrical mode of the power grid.
The Soviet designs of turbines and energy boilers were reliable and provided power plants with equipment for more than 50 years of continuous operation. At the moment Russian power plants are among of the oldest in the world. As it was mentioned above the share of old steam turbine generation composes more than 85 %.
In many cases turbine and boiler equipment work in every possible way of operational extension. Russian producers of steam and small gas turbines allow such extensions because there are no more orders for them. Such scientific research institutions as All-Russia Thermal Engineering Institute (located in Moscow) and Polzunov Scientific and Development Association on the Research and Design of Power Equipment (based in Saint-Petersburg) deal with the problem of operational extension of turbines and boilers.

These two organizations make metal analysis to make a solution about possibility of operational extension. Microstructures of turbine and boiler metal are examined to look for different defects and cracks. Works of surface recovery for turbine blades, rotor shaft, rotor disks and other details are made for them. For instance, last steam turbine stages are covered with stellite coating or laser / electro spark surface hardening.
Russian power generation companies have considerable experience in operational extension of turbine details. However, while repairing steam turbines it is necessary to replace such details as steam distribution blocks (check valves, control valves), nozzle apparatus, diaphragms, rotor blades, seal rings, rotor wheels and other details of steam turbines.

During the Soviet period steam turbines production and supply of spare parts for them was done by turbine manufacturers. But after collapse of the USSR serial steam turbine production was stopped. After that manufacture of details and blocks for repair and overhaul decreased considerably.
Gradually production of turbine details was replaced by small enterprises. They started to manufacture details for steam turbines. Such turbine repair firms work by contracts with power generation companies.
These small firms have been producing turbine components in the course of many years. They have good experience in this field. Such enterprises have narrow specialization and therefore produce only special kinds of turbine spare parts. For instance, they manufacture only rotor blades or nuts and housing pins. A turbine company can produce only details of steam distribution including an axle box with slide valves or other types of details.
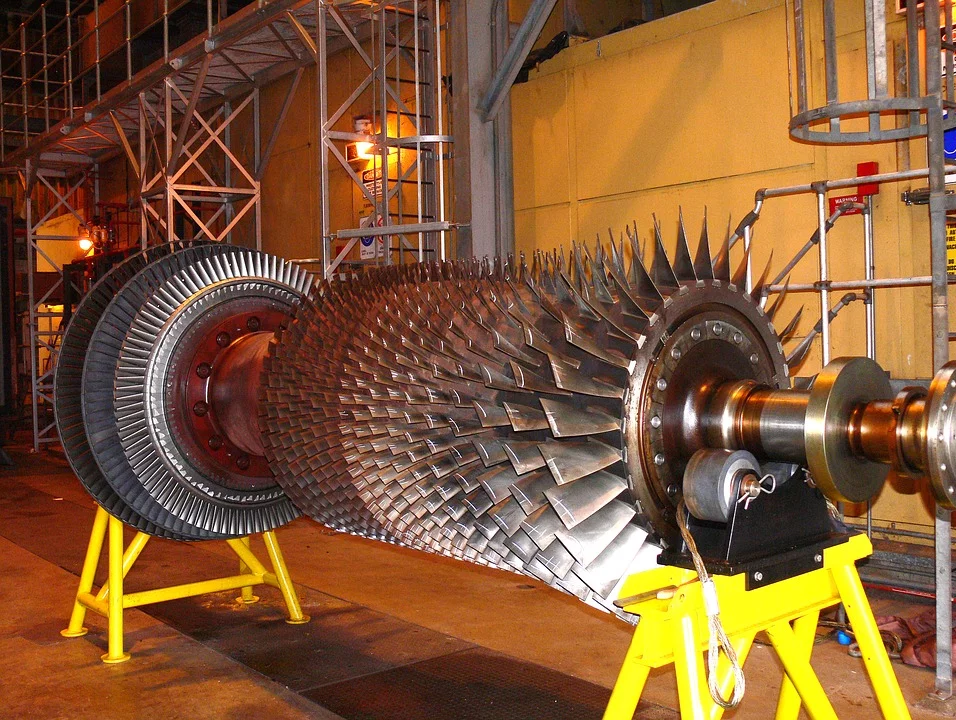
In most cases power generation companies with steam and gas turbines purchase the whole quantity of turbine spare parts for repair works. Producers have to supply full scope of spare parts in case of big tenders with a great variety of turbine components. But supplying companies are not able to produce all kinds of spare parts for steam and gas turbines. They make only those turbine details which they can and purchase other spare parts from their partners.
Division of supply in different types of turbine spare parts could be profitable for all participants. Such division can help to reduce expenditures for production and purchase of turbine spare parts. The process of supply can become more controlled and predictable in relation of delivery terms in this case.
Companies supplying turbine details take many risks for themselves in many contracts. These risks are connected with the supply of turbine details by a definite date. This date is strongly linked with the beginning of turbine overhaul and repair works. When a supplying company doesn’t produce some types of turbine details the risks of breaking delivery deadline will be higher for all participants: suppliers, turbine repair contractors and power plant operators.

The main problem in this case is that supplier of turbine details has no full and reliable information about spare parts production from its subcontractor. Usually there is no clear picture of delivery terms for both supplier and purchasing company.
In addition, the system of preventive maintenance at power plants practically doesn’t exist in Russia anymore. Power plants don’t have their own repair teams as it used to be in the Soviet Union.
At that time repair teams of power plants possessed full information about repair and overhaul history for each turbine. Power plants had qualified personnel with experience and knowledge of repair works for every turbine at a power plant. These specialists could plan repair works in a proper way and in advance.

When power plants have such turbine repair departments in their structure the specialists can anticipate most of problems in advance. Then they can help to order needed turbine blocks beforehand for the following turbine overhaul and repair procedures.
But in most cases even large power generating companies often face problems while opening a turbine housing. After this procedure they usually find additional units which require urgent repair works as well. As a rule there are no such turbine units at a spare parts stock. And that’s why the expected delivery time will be quite long.
In this case repair of the turbine unit cannot be finished during the period announced to the electrical grid operator. The period should be either changed or turbine repair should be finished without repair of the unit. Spare parts replacement can be completed later, after delivery of the needed details or the turbine unit can be repaired with the next turbine opening.
The existing difficulties of turbine repairs and overhauls require development of a new approach for their renovation from power plant operators.
Despite all these difficulties and insufficient financing of the power generating branch some companies have modern combined cycle blocks. They include big gas turbines and contain almost all the equipment produced by foreign manufacturers. These power blocks are rather different in project design. The spare parts for this equipment have never been produced in Russia.

The problem is especially difficult with spare parts for big gas turbines which have operational period not like for steam turbines. It refers to air filters of gas turbines, compressor blades, rotor blades and guide vanes of the hot turbine parts.
Usually power generating companies don’t have documentation for spare parts of such gas turbines. Transfer of this documentation is not included in contacts for gas turbines supply.
It is supposed that big foreign gas turbine manufacturers will hardly transfer documentation for spare parts production. Foreign turbine producers have a goal for sales in Russia and other countries. They are interested in sales of modern steam and gas turbines with their technologies but not for transfer of documentation for their production.
Currently Russia is looking for a solution of import substitution and decrease dependence from foreign turbine manufacturers. There are two ways of solving the problem of Russian technological dependence.
The first one is the supply of turbine details from the companies which are manufacturers of turbine components. Such small private manufacturing enterprises are located in Europe. Large corporations sometimes place orders at the same factories as well.

Establishment of long term cooperation with such manufacturing companies can be an important element of this approach for turbine repair and spare parts production. Such a cooperation will help to accumulate necessary competencies for planning of similar production facilities in Russia.
The second way is the so called reverse engineering. A plant can produce turbine components after their analysis and develop technology for their production.
Both approaches allow to organize manufacturing of components for big gas turbines which aren’t produced in Russia at the moment.
It should be mentioned that both approaches for import substitution of gas turbine components are very expensive. It refers both to resources and time spent on their implementation.
Compressorturbo supplies spare parts for steam turbines (T-250/300-240, T-100-130, T-110/120-130, T-50-90 of Ural Turbine Works) and gas turbines (General Electric MS5002E, Siemens SGT-5-2000E, GTT-3M, GTT-12):
– rotor blades;
– guide vanes;
– sets of blades;
– segments of blade bandages;
– nozzle/guide vane disks;
– diaphragms;
– rotor discs;
– rotors wheels
– rotors;
– turbine parts of steam inlet.